In the digital landscape of late 2024 and 2025, the foundation of any successful high-traffic website or enterprise application is its hosting infrastructure. As a top-tier tech writer who has overseen dozens of server migrations for high-value clients, I know that the decision between a Virtual Private Server (VPS) and a Dedicated Server is not just technical. It is financial and strategic. Your choice dictates your site’s speed, security posture, and ultimately, your revenue potential.
- The Evolution of Hosting Architecture in 2025
- Detailed Performance Comparison: Metrics That Matter
- 1. CPU Availability and Processing Power
- 2. Disk I/O and Storage Latency
- 3. Network Throughput and Port Speed
- 4. Security and Compliance
- The Financial Reality: Cost Efficiency vs. Value
- 7 Critical Signs You Need to Upgrade to a Dedicated Server
- 1. High “Time to First Byte” (TTFB)
- 2. Frequent Database Connection Errors
- 3. Traffic Spikes Cause Downtime
- 4. You Need Custom Kernel Modules or Virtualization
- 5. Data Privacy Requirements
- 6. The “Noisy Neighbor” is Slowing You Down
- 7. You Are Paying Over $150 for a VPS
- Managed vs. Unmanaged: Choosing Your Management Level
- Step-by-Step Migration Checklist: Moving from VPS to Dedicated
- Best Practices for Dedicated Server Security in 2025
- Future Trends: Bare Metal Cloud and Hybrid Hosting
- Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Growth
This comprehensive guide delves deep into the architecture, performance metrics, and financial implications of upgrading your hosting environment. We will analyze the critical tipping points where staying on a VPS becomes a liability and moving to bare metal becomes a necessity for enterprise growth.
The Evolution of Hosting Architecture in 2025
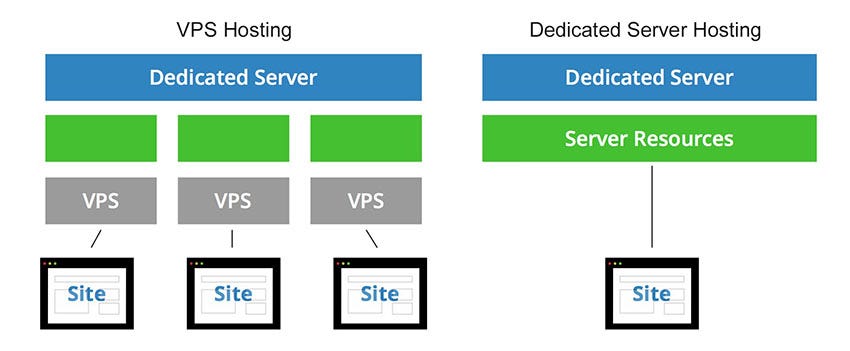
Before we compare the two, it is vital to understand what is happening under the hood. The web hosting industry has evolved significantly. The lines between high-end VPS and entry-level dedicated servers are blurring due to advancements in virtualization technology like KVM (Kernel-based Virtual Machine) and containerization. However, the fundamental difference in resource isolation remains the primary factor for high-performance web hosting.
Defining the Virtual Private Server (VPS)
A VPS is a masterful illusion of independence. It runs on a powerful physical server that is sliced into multiple virtual environments using software called a hypervisor. In 2025, the most common hypervisors are KVM and VMware ESXi.
When you purchase a VPS, you are buying a slice of the pie. You get a guaranteed allocation of CPU cores, RAM, and storage space. Unlike shared hosting, your neighbors cannot easily steal your resources, but you still share the underlying motherboard, network interface cards (NICs), and power supply units.
Key Technical Characteristics of Modern VPS:
- Virtualization Type: Hardware-level virtualization (KVM) is the standard for high-performance VPS, offering better isolation than OS-level virtualization (OpenVZ).
- Scalability: You can often upgrade RAM or CPU with a single click in your dashboard.
- Noisy Neighbor Effect: While minimized in modern cloud VPS, extreme load on the host node can still impact disk I/O latency.
Defining the Dedicated Server
A Dedicated Server is exactly what it sounds like. It is a physical server often referred to as “bare metal” that is leased exclusively to a single tenant. There is no hypervisor layer eating up CPU cycles. There are no neighbors. Every gigahertz of processing power, every byte of RAM, and every IOPS (Input/Output Operations Per Second) from the NVMe drives belongs to you.
Key Technical Characteristics of Dedicated Servers:
- Single Tenancy: You have total control over the hardware hardware.
- Customization: You can choose specific hardware components, such as enterprise-grade Intel Xeon or AMD EPYC processors and ECC (Error Correcting Code) RAM.
- Security: Physical isolation eliminates risks associated with hypervisor vulnerabilities or side-channel attacks like Spectre/Meltdown from neighboring tenants.
Detailed Performance Comparison: Metrics That Matter
When evaluating high-performance web hosting for business, we need to look at four specific metrics: CPU Steal, I/O Wait, Network Throughput, and Memory Management.
1. CPU Availability and Processing Power
On a VPS, you are often allocated “vCPUs” (virtual CPUs). In many budget or standard tier VPS plans, these are shared threads. If your site needs to crunch a massive database query, you might find that the physical core is busy handling requests for another client on the same node. This introduces “CPU Steal,” a metric that measures the time your virtual machine waits for the physical CPU to serve it.
On a Dedicated Server, CPU Steal is effectively zero. If you lease a server with a 64-core AMD EPYC processor, all 128 threads are waiting for your command. This is critical for computational-heavy tasks like real-time data analytics, machine learning model inference, or high-volume e-commerce transaction processing.
2. Disk I/O and Storage Latency
Storage performance is often the bottleneck for dynamic websites. Modern hosting relies heavily on NVMe SSDs.
- VPS: Your storage is usually a virtual disk file sitting on a large RAID array shared by hundreds of other VPS instances. If twenty other users decide to run backups simultaneously, your read/write speeds will drop, causing your application to hang.
- Dedicated: You have direct access to the disk controller. You can configure your own RAID 10 array for maximum speed and redundancy without worrying about anyone else’s I/O load. For database-heavy applications (MySQL, PostgreSQL, MongoDB), the low latency of local, dedicated NVMe storage is unbeatable.
3. Network Throughput and Port Speed
Bandwidth is not just about the monthly data transfer limit (e.g., 5TB or Unmetered). It is about the size of the pipe the port speed.
Most VPS plans come with a shared 1Gbps uplink. If the host node has a 10Gbps connection but hosts 50 active high-traffic VPS containers, your actual available bandwidth during peak hours might fluctuate wildly.
Enterprise dedicated servers often come with a dedicated 1Gbps, 10Gbps, or even 25Gbps uplink. This ensures that during a traffic spike or a marketing campaign, your server can push data out to visitors as fast as the internet backbone can take it.
4. Security and Compliance
Security is a major driver for upgrading. While VPS environments are secure, they technically present a larger attack surface due to the hypervisor layer.
- Compliance: If your business handles sensitive data requiring HIPAA (healthcare), PCI-DSS (credit cards), or GDPR (EU data privacy) compliance, a dedicated server is often the preferred choice. Auditors prefer the physical isolation of data. It is much easier to prove that no unauthorized party has access to a drive when you are the only one with physical access to the machine’s controller.
- DDoS Mitigation: High-end dedicated hosting providers offer hardware-level firewalls and DDoS protection that sit in front of your server, scrubbing malicious traffic before it hits your network interface.
The Financial Reality: Cost Efficiency vs. Value
The pricing model for web hosting has shifted in 2025.
VPS Pricing Structure:
VPS hosting is generally OpEx (Operating Expense) friendly. You pay a low monthly fee, often starting from $20 to $100 per month for a decent managed VPS. It is excellent for startups and small-to-medium businesses (SMBs) where cash flow is tight.
Dedicated Server Pricing Structure:
Dedicated servers require a higher monthly commitment, typically starting at $150 and going up to $1000+ per month for high-end configurations. However, the price-to-performance ratio often favors dedicated servers at the higher end.
Example:
A high-end Cloud VPS with 32GB RAM and 8 vCPUs might cost $160/month.
A dedicated server with 64GB RAM and 12 physical cores might cost $180/month.
For just $20 more, you get double the RAM and significantly more processing power without the virtualization overhead. This is where the “value” of dedicated hosting shines for established businesses.
7 Critical Signs You Need to Upgrade to a Dedicated Server
How do you know it is time? As a server administrator, I look for these specific red flags in the server logs and performance monitoring tools.
1. High “Time to First Byte” (TTFB)
If your website optimization is perfect images compressed, code minified, caching enabled but your TTFB is still over 500ms, your server is struggling to generate the initial HTML response. This usually means the CPU is overwhelmed.
2. Frequent Database Connection Errors
Seeing “Error establishing a database connection”? This often happens when your MySQL or MariaDB service runs out of RAM and is killed by the operating system’s OOM (Out of Memory) killer. If you have already optimized your database queries and this still happens, you need the massive RAM availability of a dedicated server.
3. Traffic Spikes Cause Downtime
A VPS can handle steady traffic well. It struggles with sudden concurrency. If you send an email newsletter or run a Black Friday ad and your site crashes immediately, your VPS hit its resource limits. Dedicated servers provide the headroom needed for these surges.
4. You Need Custom Kernel Modules or Virtualization
Some advanced software requires you to modify the operating system kernel or run your own virtualization (running a VPS inside your server). Most VPS providers block this. A dedicated server gives you “Root” access to the bare metal, allowing you to install anything, including custom OS kernels.
5. Data Privacy Requirements
As mentioned earlier, if you are storing medical records or high-security financial data, the shared nature of a VPS might violate your internal risk assessments or external regulations.
6. The “Noisy Neighbor” is Slowing You Down
If your server performance varies wildly at different times of the day without a change in your own traffic, you are suffering from noisy neighbors. This unpredictability is unacceptable for serious businesses.
7. You Are Paying Over $150 for a VPS
Once your VPS bill crosses the $120-$150 mark, you are likely overpaying for virtual resources. At this price point, the raw hardware of a dedicated server offers a better Return on Investment (ROI).
Managed vs. Unmanaged: Choosing Your Management Level
When upgrading to a dedicated server, you will face a choice: Managed or Unmanaged.
Unmanaged Dedicated Hosting
- For whom: System Administrators, DevOps Engineers, Tech-savvy businesses.
- What you get: Power, Ping, and Pipe. The host ensures the hardware works and the internet is connected. You are responsible for installing the OS, security patches, firewalls, and fixing things when they break.
- Pros: Cheaper, total control.
- Cons: If you delete a critical file, it is on you.
Managed Dedicated Hosting
- For whom: Business owners, Digital Agencies, E-commerce stores.
- What you get: A team of experts who handle the technical details. They install the OS, set up the control panel (cPanel/WHM, Plesk), monitor for security threats, and perform backups.
- Pros: Peace of mind, 24/7 expert support, hands-off maintenance.
- Cons: More expensive (usually adds $30-$100/mo to the bill).
For most businesses generating revenue, Managed Dedicated Server Hosting is the gold standard. It allows you to focus on your content and sales while the hosting company ensures the infrastructure stays online.
Step-by-Step Migration Checklist: Moving from VPS to Dedicated
Migrating to a dedicated server is a major operation. Here is the protocol I use to ensure zero data loss and minimal downtime.
Phase 1: Planning and Provisioning
- Audit Current Usage: Check your current disk space and RAM usage. Provision a dedicated server with at least double your current needs to allow for growth.
- Select the Right Stack: Choose an Operating System (AlmaLinux, Ubuntu, Debian) and Control Panel (cPanel, Plesk) that matches your current environment to make transfer easier.
- Lower TTL (Time To Live): 24 hours before migration, lower your DNS TTL to 300 seconds. This ensures that when you switch the IP address, the world sees the new server almost instantly.
Phase 2: The Data Transfer
- Initial Sync: Use tools like
rsyncor the “Transfer Tool” in WHM to copy all data from the VPS to the Dedicated Server. Keep the VPS live during this process. - Environment Configuration: Replicate your PHP settings, Apache/Nginx configurations, and firewall rules on the new server.
- Testing: Access the new server via its temporary IP address. Test every page, form, and checkout process. Ensure databases are connecting correctly.
Phase 3: The Switch
- Maintenance Mode: Put your website in maintenance mode to stop new orders or comments.
- Final Sync: Run the
rsyncone last time to catch any data that changed during the testing phase. - DNS Update: Update your domain’s A Records to point to the new Dedicated Server IP.
- Verification: Watch the logs on the new server. You should see traffic starting to flow in.
- Decommission: Keep the old VPS running for at least 7 days as a backup before cancelling.
Best Practices for Dedicated Server Security in 2025
Owning a dedicated server means you possess a powerful weapon. If compromised, hackers can use it to launch massive attacks. Security is not optional.
- Change Default SSH Port: Move SSH from port 22 to a custom port to stop automated brute-force scripts.
- Disable Root Login: Create a sudo user and disable direct root login via SSH.
- Use SSH Keys: Disable password authentication entirely and rely on SSH keys.
- Configure a Software Firewall: Use CSF (ConfigServer Security & Firewall) or UFW (Uncomplicated Firewall) to block all unused ports.
- Install Malware Scanning: Tools like Imunify360 or Maldet are essential for detecting malicious scripts uploaded to your site.
- Off-Site Backups: Never store your only backups on the same drive as your live data. Use a remote backup solution (like AWS S3 or a separate backup server).
Future Trends: Bare Metal Cloud and Hybrid Hosting
As we look toward the future of hosting, the “Bare Metal Cloud” is gaining traction. This hybrid approach allows you to provision dedicated servers with the flexibility of the cloud. You can spin up a physical server in minutes via an API, pay hourly, and destroy it when done.
This is ideal for businesses with predictable seasonal spikes. For example, an e-commerce store could run on a strong VPS for 10 months of the year and spin up two additional Bare Metal servers for November and December to handle holiday traffic, load balancing the traffic between them.
Conclusion: Making the Right Choice for Your Growth
The decision to move from VPS vs Dedicated Server is a milestone in your business journey. It signifies that you have outgrown the “starter” phase and are entering the “enterprise” phase.
While a VPS offers an incredible balance of cost and performance for growing sites, there is a ceiling. When you hit that ceiling manifested by slow load times, security concerns, or instability the dedicated server is the only logical step up.
The investment in a dedicated server is an investment in your user experience. Faster sites rank better in search engines, convert more visitors into customers, and build higher brand trust. If your website is your primary revenue generator, do not strangle it with insufficient resources. Give it the power of bare metal, and watch your business soar.